Optimasi Parametrik Minyak Pirolisis dan Karbon Sisa Hasil Pirolisis Ban Bekas dalam Reaktor Atmosfer Inert
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55679/pistonjt.v10i2.129Keywords:
Waste tire pyrolysis, Parameter optimization, Pyrolysis oil, Inert atmosphere, Alternative fuelAbstract
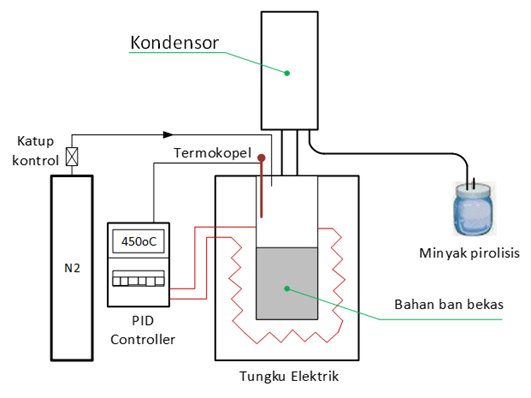
Waste tires represent a significant environmental challenge that requires sustainable solutions through conversion into energy. One of the waste treatment technologies involves a pyrolysis process that converts solid waste into liquid fuels and solid material for backfill. This study aims to optimize the process parameters for the pyrolysis of waste tires in an inert atmosphere reactor to maximize the yield and quality of liquid and solid products. Experiments were conducted by varying temperature (400, 450, 500°C) and residence time (10, 15, 20 minutes) using controlled cubic-shaped tire samples. The results indicate that the optimal operating conditions were achieved at 450°C and 15 minutes, producing a pyrolysis oil yield of 48.3% with a high calorific value of 44.6 MJ/kg, along with a solid char yield of 35.2%. he produced solid char has potential applications as a filler material in civil construction materials. Further analysis revealed significant energy conversion efficiency of the process. These findings provide a strong technical foundation for developing commercial-scale pyrolysis technology that effectively manages tire waste while producing quality alternative fuels
Downloads
References
WBCSD, “Global Tire Waste Management Report 2023. Geneva: World Business Council for Sustainable Development.” 2023.
T. Iskandar and A. C. K. Fitri, “Asap Cair dan Biochar hasil Proses Pyrolisis Sekam Padi dan Biomassa lainnya sebagai Income Generating Unit di Universitas Tribhuwana Tunggadewi,” JAST J. Apl. Sains dan Teknol., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 81–87, 2018.
B. Tian, J. Wang, Y. Qiao, H. Huang, L. Xu, and Y. Tian, “Understanding the pyrolysis synergy of biomass and coal blends based on volatile release, kinetics and char structure,” Biomass and Bioenergy, vol. 168, p. 106687, Jan. 2023, doi: 10.1016/J.BIOMBIOE.2022.106687.
X. Li et al., “A Study on the Pyrolysis Behavior and Product Evolution of,” Catalysts, vol. 14, no. 200, pp. 1–20, 2024.
KLHK, “Statistik Pengelolaan Limbah Bahan Berbahaya dan Beracun 2022. Jakarta,Kementerian Lingkungan Hidup dan Kehutanan Republik Indonesia.” 2023.
B. Skariah and R. C. Gupta, “A comprehensive review on the applications of waste tire rubber in cement concrete,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 54, pp. 1323–1333, 2016, doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.10.092.
M. Hashamfirooz and M. Hadi, “Heliyon A systematic review of the environmental and health effects of waste tires recycling,” Heliyon, vol. 11, no. 2, p. e41909, 2025, doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41909.
J. Pendidikan, M. Sains, and M. Pirolisis, “Perbandingan kualitas bahan bakar dari pengolahan sampah plastik menjadi bahan bakar minyak dengan metode pirolisis,” EduMatSains, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 219–230, 2021.
R. T. Aziz et al., “BAHAN PRODUKSI GAS ASAP CAIR MELALUI METODE PIROLISIS,” vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 73–82, 2022.
J. P. Simanjuntak, R. Siahaan, and A. N. Putra, Teknologi Pirolisiis Biomassa-Energi Terbarukan. 2024.
Z. Cepic, V. Mihajlovic, S. Duric, M. Milotic, M. S. STepanov, and M. I. Micunovic, “Experimental Analysis of Temperature Influence on Waste Tire Pyrolysis,” Energies, vol. 14, no. 5403, 2021, doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175403 1.
M. Pahnila, A. Koskela, P. Sulasalmi, and T. Fabritius, “A Review of Pyrolysis Technologies and the Effect of Process Parameters on Biocarbon Properties,” Energies, vol. 16, no. 6936, pp. 1–27, 2023.
K. Kumar and N. . Panwar, “Pyrolysis technologies for biochar production in waste management : a review,” Clean Energy, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 61–78, 2024.
W. H. Chen, Naveen C, P. K. Ghodke, A. K. Sharma, and P. Bobde, “Co-pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass with other carbonaceous materials: A review on advance technologies, synergistic effect, and future prospectus,” Fuel, vol. 345, p. 128177, Aug. 2023, doi: 10.1016/J.FUEL.2023.128177.
R. Cherba, K. Wróblewski, and E. Molga, “PYROLYSIS OF WASTE TYRES – THE EFFECT OF REACTION,” Chem. Process Eng., vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 363–377, 2017, doi: 10.1515/cpe-2017-0028.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Lukas Kano Mangalla, Agustinus Lolok, Samhuddin Samhuddin, La Ode Ahmad Barata

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.








